Composition of photovoltaic systems
Photovoltaic systems are categorized into independent power generation systems and grid-connected power generation systems. The former generates electricity for a family in a remote area, and the excess electricity can be stored in batteries. This system consists of solar panels, inverters, brackets, transformers, and electronic components. The grid-connected power generation system includes independent photovoltaic power stations and roof-mounted systems, which can integrate excess electricity into the national power grid; therefore, this type of system does not require batteries. The inverters used in these two forms differ: off-grid inverters and grid-connected inverters. The most important component in a photovoltaic system is the solar panel, which converts solar energy into direct current. Solar panels are divided into crystalline silicon panels (monocrystalline silicon panels, and polycrystalline silicon panels), amorphous silicon panels, and thin-film panels. Since crystalline silicon panels are still the most widely used, only crystalline silicon panels are discussed here.
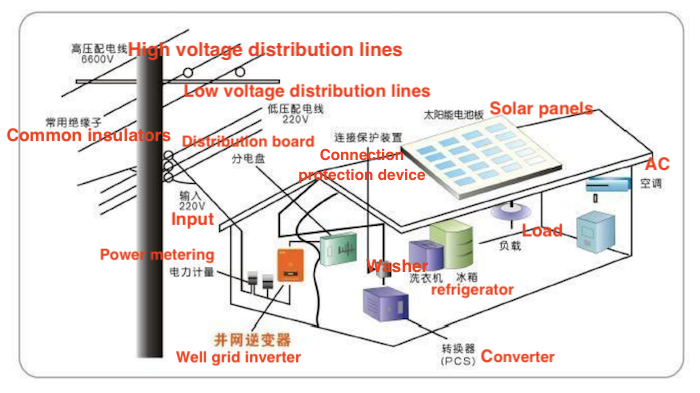
Figure 1 Diagram of grid-connected PV systems
Figure 1 shows the appearance of monocrystalline silicon panels and polycrystalline silicon panels. The left shows monocrystalline silicon panels. Due to the different atomic arrangements of monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon, their appearance differ. Except for the different silicon wafers, the other components of these two panels are the same, including aluminum alloy frames, low-iron tempered glass, EVA films, solar wafers, and TPT back films.
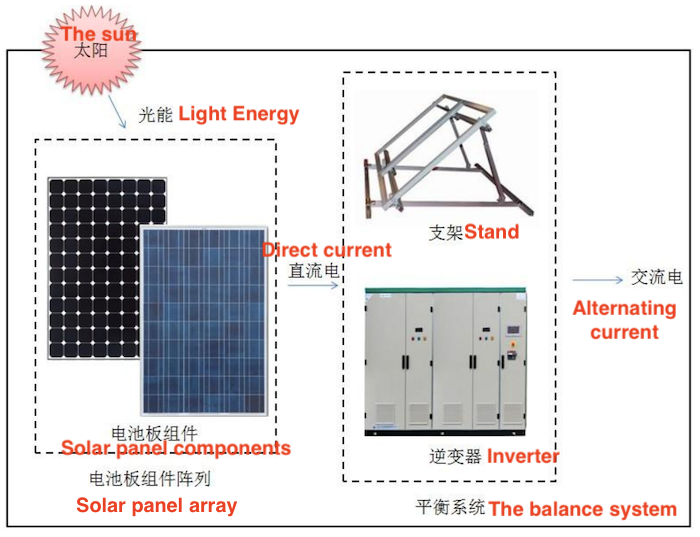
Figure 2 Main parts of a PV system
Figure 3 Section schematic of a silicon panel
A solar panel is mainly composed of aluminum frames, glass, EVA, silver coatings, aluminum coatings, anti-reflection layers, silicon wafer, and a TPT backplane. The silicon wafers, silver coatings, aluminum coatings, and anti-reflection layers collectively form the solar cells, which are processed from silicon wafers.
Generally speaking, there are two sizes of solar panels: one composed of 60 silicon wafers and the other composed of 72 silicon wafers. Here, we use a panel with 60 silicon wafers as an example to explain the weight ratio of each component. Due to differences in raw materials from different manufacturers and the variations in available data, we refer to the 2007 data of 210 Wp collected by de Wild for Europe and the United States, which has good reliability, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Material weight distribution of crystalline silicon solar panels
| Materials | Weight kg/piece | Ratio % |
| Aluminum frames | 4.20 | 17.74 |
| Glass | 16.10 | 68.02 |
| EVA | 1.60 | 6.76 |
| Silicon wafer | 0.82 | 3.46 |
| TPT backplanes | 0.83 | 3.51 |
| Aluminum coatings | 0.11 | 0.46 |
| Silver coatings | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Anti-reflection layers | a | a |
| Total | 23.67 | 100 |
As shown in Table 1, the weight of glass accounts for 68.02% of the total, which is much higher than other components, followed by aluminum frames. These two components make up 85.76% of the weight of the solar panel. The consumption of silicon wafers is relatively small, making up only 3.46% of the total weight. Although they are light, silicon wafers are the most important component of the solar panel.
Working principles of photovoltaic systems
Photoelectric conversion: Photovoltaic modules absorb sunlight and convert light energy into direct current (DC).
Electric energy conversion: The inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for use in homes or power grids.
Electric energy storage (optional): Excess electrical energy is stored in the battery energy storage system for subsequent use.
Power transmission: The alternating current (AC) converted by the inverter is transmitted to the power equipment or power grid through the distribution network.
Development prospects of photovoltaic systems
With continuous advancements in technology and reduced production costs, photovoltaic systems have been widely adopted around the world. Governments of various countries also support the development of the photovoltaic industry through policies and subsidies. In the future, with advancements in energy storage technology and the popularization of smart grids, photovoltaic systems will play an increasingly important role in the global energy structure, achieving true sustainable development.