China's energy structure is dominated by coal, and China is the world's largest coal producer and consumer. Moreover, China has become the world's second-largest oil consumer after being a net oil exporter in the early 1990s, second only to the United States. As can be seen from Figure 1, fossil energy (coal, oil and natural gas) accounts for approximately 93% of China’s energy consumption, of which coal accounts for 71%. This is an energy pattern that is far different from that of the EU and the United States. Considering the large population in China, China’s energy crisis is relatively more severe. We must realize that China's existing energy structure must be changed and we should gradually turn to the future energy structure.
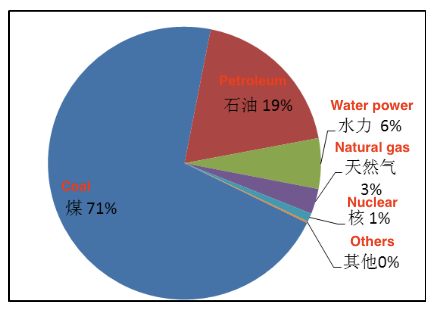
Figure 1 China’s energy consumption ratio
Although China has been actively building nuclear power plants and developing various renewable energy sources in recent years, coal power will continue to dominate in the medium to long term. However, when generating 1 kilowatt hour of electricity, there will be 1kg of carbon dioxide emissions and other greenhouse gases and pollutants. Because coal consumption accounts for a large proportion, China's carbon dioxide emission intensity is relatively high. SO2 and soot emissions from conventional coal burning account for approximately 70 to 80% of total emissions. Moreover, China's greenhouse gases mainly come from the combustion of fossil fuels. The relatively backward coal production and consumption have increased the pressure on environmental protection. If this situation continues, it will bring greater threats to China's already fragile ecological environment. The sustainable development of the living environment has become a basic issue in the development of contemporary society. Protecting the environment, rationally utilizing natural resources, reducing energy consumption and providing a healthy and comfortable living environment have become hot topics.
In contrast, solar energy is a widespread, sustainable source of energy and its applications are generally environmentally friendly. However, it has a series of serious shortcomings. It has a relatively low energy density. On a sunny day, the highest density on the earth's surface is generally about 1kW). It also has features of intermittency (only available during the day) and uneven distribution (mostly distributed between 30° latitude north and 30° latitude south). If you want solar energy to become one of the main energy suppliers, it must be converted into other forms, such as electricity or heat.
China’s solar energy
China has emerged as a global leader in solar energy, with its rapid growth and development in this sector. China’s commitment to renewable energy sources has been driven by several factors, including its need to reduce its heavy reliance on fossil fuels, combat air pollution, and meet its growing energy demands. One of the key reasons behind China’s success in solar energy is its government’s strong support and favorable policies. The Chinese government has implemented various measures to promote the use of solar power, such as providing subsidies for solar installations and setting ambitious targets for renewable energy capacity. These policies have attracted significant investments from both domestic and international companies, leading to a boom in the solar industry.
China’s manufacturing capabilities have played a crucial role in the growth of its solar sector. China is known for its large-scale production of photovoltaic panels and other components required for solar power generation. This mass production has led to a reduction in costs, making solar energy more affordable and accessible. In addition to domestic consumption, China has also become a major exporter of solar panels and related products. Its competitive prices have made it an attractive option for countries looking to adopt clean energy solutions.
However, despite these achievements, there are challenges that China faces in sustaining its leadership position in the global solar market. One major concern is overcapacity – with so many manufacturers producing panels at low costs, there is a risk of oversupply leading to price wars and reduced profitability. Another challenge lies in integrating intermittent renewable sources like solar into the existing grid infrastructure. As more solar installations come online, ensuring efficient transmission and distribution becomes crucial.
In conclusion, China’s success story in the field of solar energy can be attributed to strong government support, favorable policies, manufacturing capabilities at scale, and competitive pricing. However, addressing challenges such as overcapacity management and grid integration will be vital for sustaining this growth trajectory. Nonetheless, China's commitment to renewable energy is commendable and serves as an inspiration for other nations to follow suit.